A guide to building support agents that combine technical rigor with emotional intelligence.
“Please wait, you are in queue.” It is the one line no one wants to hear and yet, it lingers in far too many customer journeys. In a world where technology can predict, personalize, and respond in real time, waiting behind an IVR or a scripted bot is not just frustrating; it is out of step. Customers have moved on. They expect interactions to feel natural, intelligent, and attuned, not mechanical. For businesses, this is not a matter of catching up, it is a mandate to lead. And at the heart of that shift are GPT customer agents, designed to deliver experiences that are conversational, context aware, emotionally intelligent and secure.
Where is the Gap Between Logic Trees and Conversations
Traditional support systems were built to manage volume. Rule-based bots and scripted workflows handled routine queries by following decision trees and keyword matches. They were effective for answering common questions, but often failed to grasp nuance, carry context or adapt to follow-up interactions.
GPT customer agents represent a clear break from that model. These systems are powered by generative language models capable of interpreting intent, drawing from real-time context and generating responses that are relevant, human-like, and situationally aware. The interaction stops being a transaction and starts becoming a conversation.
What It Takes to Get It Right
Turning that conversation into something consistent and valuable takes more than a powerful model. It calls for clarity on what the agent should handle, how it should adapt, and where it should escalate. The strength of the experience depends on how well the technology is shaped around real moments of need. When the design gets that right, the agent does more than respond. It earns its place.
Here is a guide shaped by MResult’s experience delivering GPT customer agents in complex, real-world environments.
How To Drive the Shift: A Practical Guide to Building GPT Customer Agents
Designing a GPT customer agent is not a single step implementation. It is a series of decisions that shape how the system listens, responds, and evolves. Here’s an eight step guide offering a grounded way to build capability without losing control.
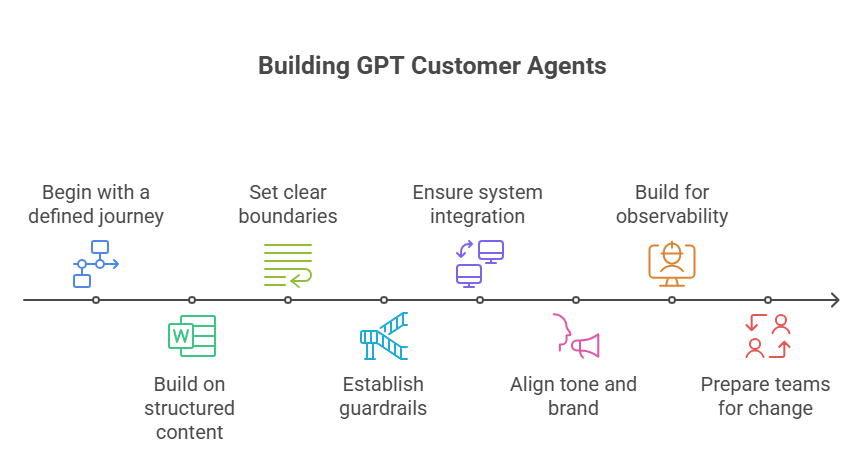
- Begin with a defined journey Start with a customer journey that sees high volume or friction such as onboarding, post-purchase support or policy clarification. Deploy the agent where it can make the most immediate impact whether on the website, mobile application, or messaging platform. For example, helping customers navigate plan selection on the website or reschedule appointments through the app. Once effectiveness is established, expand the agent across other journeys and channels in a structured way.
- Build on structured, reliable content Prepare the foundation with policy documents, process flows, and frequently asked questions. Review and organize them for clarity and consistency. The agent depends on clean inputs. Clear, well-structured content reduces the risk of vague responses and improves reliability.
- Set clear boundaries and accountability Define what the agent will handle, where it will escalate, and how performance will be measured. Assign roles for oversight and create a matrix to track ownership, response quality and exceptions. Use real-time observability to ensure the agent stays aligned with intent.
- Establish guardrails from the beginning Address privacy, consent and compliance early. Build the experience within the bounds of internal policies and applicable regulations. For example, when guiding a patient through a clinical trial or helping a candidate understand study eligibility, the agent must protect personal data and preserve context. Every interaction must feel secure.
- Ensure integration with core systems Connect the agent to internal platforms such as knowledge bases, customer profiles and case management tools. This enables the agent to respond with relevant information and take meaningful actions without disconnecting from existing workflows.
- Align tone, behavior, and brand Shape the agent’s voice to reflect how the business wants to be experienced. Define its personality, language style and boundaries. Whether the tone is formal, warm or concise, the agent must sound intentional and consistent across all touchpoints.
- Build for observability and learning Track how the agent performs in live settings. Use transcripts, logs and usage patterns to understand where it struggles or repeats. Improve performance by refining prompts, updating source content, and reviewing escalation paths. Build a feedback loop that improves without losing control.
- Prepare teams for operational change A GPT agent changes how support functions operate. Communicate its role clearly. Train those who will monitor and govern its performance. Ensure teams understand how to collaborate with the agent and when to take over. A successful rollout is as much about readiness as it is about capability.
What Good Looks Like
MResult is building best-in-class GPT customer agents designed for real-world complexity and emotional nuance. Tranquilla.ai is one such example. It is an award-winning empathic AI agent initially developed for mental health support and now extended to veteran care, wellness journeys, and concierge services. It recalls past interactions, adapts to the user’s tone and responds with language that feels natural and considered. Designed to handle sensitive conversations with care, it shows how contextual memory and emotional intelligence can be embedded into everyday support experiences.
Why It Matters Now
Industry research shows that businesses using Generative AI in customer service are reporting up to 30 percent faster resolution times and double-digit improvements in customer satisfaction. Gartner projects that by 2026, more than 30 percent of all customer support interactions will be handled by generative AI systems. These numbers show what becomes possible when technology is aligned with business goals and customer expectations.
When Intelligent Support Drives Impact
The move from scripted responses to intelligent, conversational support is not a future state, it is already in motion. GPT customer agents are changing how businesses meet customer needs, build trust and scale services. But the value does not lie in the model itself. It lies in how well it is shaped, governed, and integrated. It happens when the shift is intentional, the design is sharp, and the value is real.